Access control
This section explains how eZ Publish manages user accounts and access permissions. The system comes with a built-in access control mechanism that can be used to limit access to content or to certain functions. The access control system is based on the following elements:
- User
- User group
- Policy
- Role
The following illustration shows the relations between the elements in the list above.
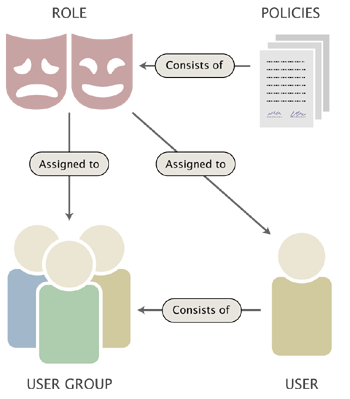
Users, groups, policies and roles.
A user defines a valid user account on the system. A user group consists of users and other user groups. A policy is a rule that grants access to content or a certain system function. For example, a policy may grant read access to a collection of nodes. A role is a named collection of policies. A role can be assigned to users and user groups. The following text gives a more in-depth explanation of the user/group/policy/role elements.
User
An actual user account is represented by a content object (with at least one node assignment) that contains information about a specific user. The default "User" class allows the storage of the following elements: first name, last name, E-mail, username and password. The last three elements (E-mail, username and password) are provided by the "User account" datatype. This is a special datatype which plugs more deeply into the system. Instances of any content class containing the "User account" datatype will function as valid users on the system. In other words, if there is a need to store additional information about users, it is possible to either modify the default user class or to create a custom class that contains the datatype.
Enabled and disabled user accounts
The user accounts can be enabled or disabled from within the administration interface. When disabled, an account will continue to exist, but the user will not be able to log in until the account is enabled. Newly created accounts are enabled by default.
Locked and unlocked user accounts
In addition to being enabled and disabled, user accounts can be locked and unlocked. An account will be automatically locked by the system if the maximum number of failed login attempts is exceeded. A failed login attempt is a combination of a valid user name and an invalid password. Once an account is locked, its owner will not be allowed to log in until the account is either unlocked by another user with administrator privileges or if the login request is coming from a trusted IP address / range.
The number of failed log-in attempts are stored in a database table called "ezuservisit". An account's failed login counter is automatically reset upon a successful log-in. In other words, as long as you log in with a valid username/password combination, the failed log-in attempt counter associated with your account will be zero.
Note that the default configuration does not allow different users to be registered with the exact same E-mail address. This is just a built-in precaution mechanism which can be easily turned off by setting the "RequireUniqueEmail" directive within the [UserSettings] block of a configuration override for "site.ini" to "false".
User ID
Every user has a unique identification number which is the same as the ID number of the actual object that represents the user account. Among other things, the user IDs are used by other objects on the system. In particular, an object contains references (by the way of user IDs) to the initial creator and to all users who have created versions within that object. Removing a user account might lead to an inconsistent state where objects have owner/modifier references to non-existing user accounts. Because of this, it is not recommended to remove users from the system, the accounts to be removed should be disabled instead.
User group
A user group is a content object (with at least one node assignment) that contains user accounts and other user groups. In other words, a user group is just a collection of users (similar to a directory containing files and sub-directories on a file system).
Policy
A policy is a rule that grants access to a specific function or all functions of a module. A policy consists of the following elements:
- Module name
- Function name
- Function limitation
The module name reveals the actual module that the policy grants access to. The function name specifies which function the policy should be limited to. A policy can either be restricted to a single function or grant access to all functions of a module. A module can have none or several functions. The functions are assigned to the module's views and thus the access requirements for a view are controlled by the functions that are assigned to that view. The function-view assignments can not be tampered with from within the administration interface. A policy granting access to a module's function can be further restricted by the way of function limitations. This can only be done if the function itself supports limitations. A function may support none, one or several limitations. The following table shows an overview of the available function limitations.
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Class |
The "Class" limitation makes it possible to limit a policy to objects of certain types. |
| Group |
The "Group" limitation makes it possible to limit a policy to objects that are owned by a group. |
| Language |
The "Language" limitation makes it possible to limit a policy to object versions in specific languages. |
| Node |
The "Node" limitation makes it possible to limit a policy to a specific node. |
| Owner |
The "Owner" limitation makes it possible to limit a policy to objects that are owned by the user who is logged in. |
| Parent class |
The "Parent class" limitation makes it possible to limit a policy based on the type of the object referenced by the parent node. |
| Section |
The "Section" limitation makes it possible to limit a policy to objects that are assigned to certain sections. |
| Siteaccess |
The "Siteaccess" limitation makes it possible to limit a policy to a certain siteaccess. |
| Status |
The "Status" limitation makes it possible to limit a policy to a certain version status (published, archived, etc.). |
| Subtree |
The "Subtree" limitation makes it possible to limit a policy to a certain part of the content node tree. |
Role
A role is a named collection of policies. A role can be assigned to users and user groups. It is possible to assign a role with additional limitations. The role limitation feature is typically useful in a case where multiple users with similar permissions have to manipulate different parts of the content node tree. Instead of creating a role for each user, the site administrator can create a generic role and assign it with different limitations to the different users. The role limitations will override the limitations of the role's policies. The following table shows an overview of the available role limitations.
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Section |
The "Section" limitation makes it possible to limit a role to objects that are assigned to certain sections. |
| Subtree |
The "Subtree" limitation makes it possible to limit a role to a certain part of the content node tree. |
Balazs Halasy (14/09/2010 10:20 am)
Geir Arne Waaler (10/06/2011 8:45 am)

Comments